
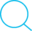
// struct name{
// actor list;
//};
struct Student{
string name;
int age;
int score; // combine many data types
};
// Three methods to initialize a struct
// 1st method
struct Student s1; // or Student s1, i.e omit data type struct is ok
s1.name = "Tom";
s1.age = 18;
ss1.score = 95;
// 2nd method
struct Student s2 = {"Jerry", 28, 75};
// 3rd method
// add struct variable name after definition
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main(){
struct Student stuArray[3] = {
{ "Tome", 18, 76},
{ "Jerry", 22, 88},
{ "Hod", 23, 92}};
stuArray[2].name = "Tim";
stuArray[2].age = 60;
for ( int i=0; i<3; i++){
cout << stuArray[i].name << stuArray[i].age << stuArray[i].score << endl;
}
return 0;
}
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main(){
struct Student s = {"Tom", 25, 100};
struct Student *p = &s; // pointer to struct must be struct type, not int *p;
student *p = &s; // here we can alse omit struct, same as last line;
cout << p->name << p->age << p->score << endl; // use -> to get struct actor value
return 0;
}
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
struct Teacher {
int id;
string name;
int age;
struct Student stu;
};
int main(){
Teacher t;
t.id = 100;
t.name = "Tim";
t.age = 50;
t.stu.name = "Tom";
t.stu.age = 16;
t.stu.socre = 60;
return 0;
}
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
// value pass
void printStudent1(struct Student s){
s.age = 100;
cout << s.name << s.age << endl;
};
// address pass
void printStudent2(struct Student *p){
p->age = 200;
cout << p->name << p->age << endl;
};
int main(){
Student s = {"Tom", 23, 85};
printStudent1(s);
printStudent2(&s); // not a pointer, just an address, but similarly, after all pointer "is" address
cout << s.age <<endl; // change of parameter in value pass doesn't change the argument value
// change of parameter in address pass change the argument value
return 0;
}
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
// value pass
void printStudent1(const struct Student *s){
//s->age = 150; // it's forbidden due to const
cout << s->name << s->age << endl;
};
int main(){
Student s = {"Tom", 23, 85};
printStudent1(&s); // address pass saves much storage than value pass
return 0;
}
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
# include <string>
# include <ctime>
struct Student {
string name;
int score;
};
struct Teacher {
string name;
struct Student stuArray[5];
};
void allocateSpace(struct Teacher tArray[], int len){
string nameSeed = "ABCDE";
for (int i=0; i<len; i++){
tArray[i].name = "Teacher_";
tArray[i].name += nameSeed[i]; // += in string
for (int j=0; j<5; j++){
tArray[i].stuArray[j].name = "Student_";
tArray[i].stuArray[j].name += nameSeed[j];
int random = rand()%61 + 40; // generate 40~100 random number
tArray[i].stuArray[j].score = random;
}
}
}
void printInfo(struct Teacher tArray[], int len){
for (int i=0; i<len; i++){
cout << tArray[i].name << endl;
for (int j=0; j<5; j++){
cout << "\t" << tArray[i].stuArray[j].name << tArray[i].stuArray[j].score << endl; // "\t" is for tab
}
}
}
int main(){
srand((unsigned int)time (NULL));
struct Teacher tArray[3];
int len = sizeof(tArray)/sizeof(tArray[0]);
allocateSpace(tArray, len);
printInfo(tArray, len);
return 0;
}
// to generate 40~ 100 random number
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
int main() {
// Set the seed for the random number generator
std::srand(std::time(nullptr));
// the seed value is set to the current time using std::time(nullptr) to ensure
// that each run of the program generates a different sequence of pseudo-random numbers.
// Generate a random number between 40 and 100, inclusive
int num = std::rand() % 61 + 40;
// Generate and print out the random integers
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
std::cout << std::rand() << " ";
}
return 0;
}
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
# include <string>
# include <ctime>
struct Hero {
string name;
int age;
string sex;
};
void allocateSpace(struct Hero tArray[], int len){
string nameSeed[] = {"liubei", "guanyu", "zhangfei", "zhaoyun", "diaochan"};
int ageSeed[] = {23,22,20,21,19};
string sexSeed[] = {"male", "male", "male", "male", "female"};
for (int i=0; i<len; i++){
tArray[i].name = nameSeed[i];
tArray[i].age = ageSeed[i];
tArray[i].sex = sexSeed[i];
}
};
void printInfo(struct Hero tArray[], int len){
for (int i=0; i<len; i++){
cout << tArray[i].name << tArray[i].age << tArray[i].sex << endl;
}
};
void BubbleSort(struct Hero tArray[], int len){
for (int i=0; i<len; i++){
for (int j=0; j<i-len-1; j++){
if (tArray[j].age > tArray[j].age){
struct Hero temp = tArray[j];
tArray[j] = tArray[j+1];
tArray[j] = temp;
}
}
}
};
int main(){
struct Hero tArray[5];
int len = sizeof(tArray)/sizeof(tArray[0]);
allocateSpace(tArray, len);
BubbleSort(tArray, len);
printInfo(tArray, len);
return 0;
}